What to know about Inspiratory Muscle Training

Training your inspiratory muscles is a course of therapy aimed at strengthening the respiratory muscles and thereby improving the breathing ability and the respiratory system.
Inspiratory muscle training (IMT) is normally aimed for people who suffer from asthma, bronchitis, COPD, and emphysema, which are people who experience trouble breathing daily due to narrow airways and swelling in their lungs. But inspiratory muscle training has also proven to be efficient in enhancing physical performance, and many people have already implemented breathing as part of their training to improve endurance and overall performance
Training the respiratory muscles
Respiratory muscle training can be defined as a technique that aims to improve the function of the respiratory muscles through specific exercises. It consists of a series of breathing exercises performed to increase the strength and endurance of the respiratory muscles and thereby improve the respiratory system.
The relation between physical activity and the respiratory muscles
The strengthening of the respiratory muscles used for breathing is necessary for improving your physical performance and level. During exercise, the demand for our body’s need for oxygen increases and therefore, our breathing volume must also increase in order to cope with the increasing demand for oxygen. This requires the muscles surrounding the lungs to come into play and contract to keep up with the increasing need for oxygen. The more intense the workout is, the more forcefully and rapidly these muscles must work.
Therefore, you will need a lot of energy to perform physically. By improving your respiratory strength, you will increase the amount of oxygen that can be inhaled in a given period, which will result in a decrease in energy consumption and enhance your endurance level.
The process of ventilation between oxygen and blood which is constantly occurring when we breathe occurs through neurological control of the respiratory muscles. Muscles related to respiration may be divided into inspiratory and expiratory muscles
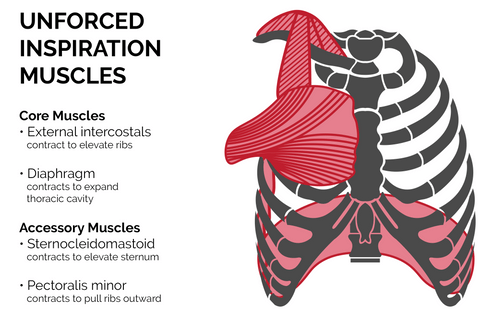
Respiratory muscle training involves both inspiratory muscle training (IMT) and expiratory muscle training (EMT). With inspiratory muscle training, we are especially able to increase the oxygen that the breathing muscles require during exercise.
Inspiratory muscle strength training
Through inspiratory muscle strength training, you will be able to become increasingly aware of your breathing, learn how to breathe more efficiently, and control the level of oxygen needed. Thereby, strengthening your endurance. Endurance is the ability to continue or last longer during physical activity, which is why it is important for improving performance. Regular inspiratory muscle training is effective for improving aerobic or cardiovascular exercise such as running or cycling, where endurance is especially important.
We typically use between 10 to 15% of our total lung capacity. With inspiratory muscle training, it is possible to increase the amount of lung capacity used. Breathing deeper requires more energy but also means that more oxygen can enter the bloodstream with each breath. So you will be able to take slower and deeper breaths and get more oxygen out of each breath, thereby reducing the amount of oxygen the breathing muscles require during exercise. As a result, more oxygen is available for other muscles in the body during a workout.
Airofit Breathing Trainer helps you perform inspiratory muscle training and increase your respiratory strength. Watch and learn about Airofit, and how our breathing trainer works to improve performance:
How does inspiratory muscle training work?
The most commonly used, researched and validated the form of inspiratory muscle training is resistance training, also called inspiratory pressure threshold loading (IPTL). By using a breathing device that contains a pressure loaded inspiratory valve and an unloaded expiratory valve you can add resistance. The level of pressure is set to fit your lung capacity and may be adjusted as you develop your technique.
How to get started:
- Using the breathing device, you start with a lung test
- Inspiratory muscle training is performed in a relaxed seated position
- Train 2-3 times per day, preferably in the morning and evening.
- Train for around 5-10 minutes per day
- Increase the breathing training time continuously
Training your inspiratory muscles can have huge benefits for your physical performance. It improves endurance and for athletes that train daily, the results can be quite significant. However, it also has a positive impact on your overall health, body, brain, and heart. Research suggests that inspiratory muscle training lowers blood pressure, improves vessel health, and improves cognitive health.




